What is HIV?
- HIV is the acronym for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus which belongs to a group of viruses called “retroviruses”
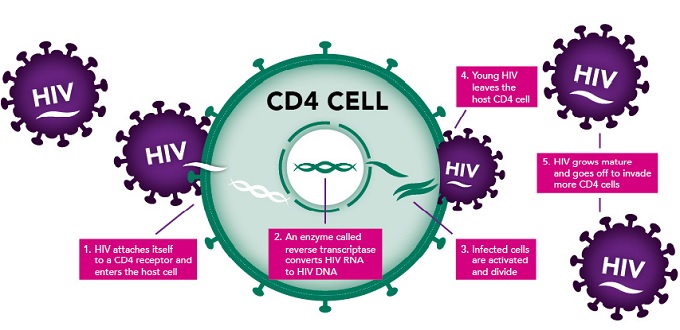
- HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as CD4 or T cells
- When CD4 cell numbers decline below a critical level, the body becomes progressively more susceptible to opportunistic infections
- With access and adherence to effective treatment, HIV is a manageable chronic condition
- All pregnant women are recommended to start on treatment and remain on it lifelong. Women should commence ART as soon as they are able to do so in the second trimester, or within the first trimester if their VL>100,000 copies /ml or CD4 cell count is less than 200 cells/mm. All women should have commenced ART by week 24 of pregnancy
Important terms
ARV/ART
- Treatment of retroviral infections like HIV is by antiretroviral drugs (ARV)
- Antiretroviral therapy (ART) , Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and combined antiretroviral therapy (cART) are terms also used
- ARV treatment does not kill the HIV virus but slows down viral replication, thereby protecting the body’s immune function. The overall aim of treatment is to suppress the virus (maintain undetectable viral load) and protect immune function (improve CD4 count)
- Until recently, UK guidelines recommended starting cART treatment at a CD4 count level of 350. However, new research evidence has reported the benefits to early cART initiation, suggesting that if individuals are able to commit to treatment, it should be started, regardless of the CD4 count.
- In pregnancy, women who have not started treatment for their own health are advised to commence combination treatment prior to 24 weeks gestation, to prevent mother to child transmission (MTCT).
Response to treatment is monitored through the following tests:
Viral load
- Viral load tests are a measurement of the progression of HIV by measuring the amount of virus in the blood. The measurements are in copies per millilitre (e.g. 10,000 copies/ml) with ‘undetectable’ considered to be below 50 copies/ml (regional variations may apply according to laboratory assays used)
- If a mother’s viral load is undetectable when her baby is born the chance of MTCT is almost zero.
CD4
- CD4 cells (also called T cells) are a type of white blood cell that fight infection. HIV destroys CD4 cells, making it harder for the body to fight infections
- The CD4 count is the number of CD4 cells in one cubic millimetre (mm3) of blood and provides an indication of how well the immune system is working
- CD4 counts vary, normal range is 400-1,600 cells/mm3, and may drop when ill or during pregnancy
- A CD4 count below 350 cells/mm3 is considered to be low

